
Artificial intelligence has taken the world by storm. Over the past few years, AI technology has transformed almost everything — from our day-to-day lives to the way we work and build careers.
Entire industries are changing. Some jobs are disappearing, new opportunities are emerging, and businesses that fail to adapt are being left behind. One thing is now clear: to succeed in the future, having a strong understanding of artificial intelligence and knowing how to use it strategically will be essential.
What many people don’t realize is that AI is not a single system. There are different types of AI and AI models, yet most of us are familiar with only a few — and as a result, we don’t take full advantage of this technology. Even more importantly, new AI models are expected to emerge in the coming years, further changing how we live and work.
I first became deeply curious about this topic after attending a seminar by Professor Henrik von Scheel, where he discussed artificial intelligence and major global developments expected in the years ahead. During the seminar, he made a statement that stood out to me:
“AI has eight models, but most people only think about one.”
That insight led me to explore the eight types of AI in depth — how they work, where they are used, and why understanding them matters. In this article, I’ve compiled the key insights from my research, along with examples and additional resources for readers who want to learn more.
Artificial intelligence is often spoken about as if it were a single technology. In reality, AI is a broad field made up of different types of systems, each with its own capabilities, limitations, and impact. Understanding these distinctions is essential for anyone working with technology, policy, business, or education.
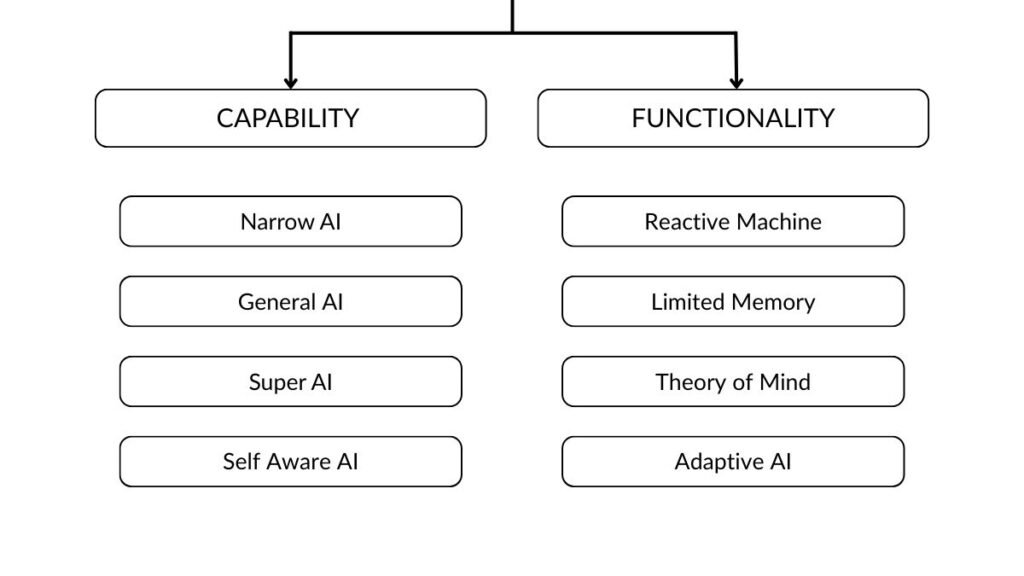
Experts generally classify AI using two complementary frameworks:
-
Capability-based classification, which focuses on how intelligent an AI system is
-
Functionality-based classification, which focuses on how an AI system operates
Together, these frameworks define the eight most widely accepted types of artificial intelligence in use or under discussion today.
Comparison of the 8 Types of AI
| Classification | AI Type | Intelligence Scope | Current Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capability | Narrow AI | Task-specific | Deployed |
| Capability | General AI | Human-level | Research |
| Capability | Super AI | Beyond human | Hypothetical |
| Capability | Self-Aware AI | Conscious | Theoretical |
| Functionality | Reactive Machines | No memory | Limited use |
| Functionality | Limited Memory | Data-driven | Widely used |
| Functionality | Theory of Mind | Social cognition | Early research |
| Functionality | Adaptive AI | Self-learning | Emerging |
I. AI Classification Based on Capabilities
This classification looks at how closely an AI system approaches human intelligence.
1. Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI)
What is it?
Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI), also known as Weak AI, is designed to perform a specific task or a narrow range of tasks extremely well. It does not possess general understanding or consciousness and cannot transfer knowledge from one domain to another.
A well-known example is a search engine. It can retrieve information efficiently, but it does not understand meaning the way humans do. Similarly, a language model can generate text but does not “know” what it is saying.
Current uses, apps, and services
ANI is everywhere:
-
Search engines and recommendation systems
-
Voice assistants and chatbots
-
Medical image analysis software
-
Fraud detection systems
-
Autonomous driving modules
Almost every AI-powered product today falls into this category.
Future predictions
ANI will continue to dominate AI development. Systems will become more specialized, faster, and more accurate, but they will remain task-focused. The biggest changes will come from combining multiple narrow systems into coordinated workflows.
2. Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
What is it?
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) refers to AI systems capable of human-level reasoning. An AGI would be able to learn new tasks, reason abstractly, and apply knowledge across domains without being retrained for each task.
There are no real-world examples of AGI today. Most portrayals exist in research papers, thought experiments, or science fiction.
Current uses, apps, and services
AGI is not currently deployed. Research is ongoing in areas such as:
-
Cognitive architectures
-
Multi-modal reasoning systems
-
Long-term memory and planning
Future predictions
AGI is likely years or decades away, if it is achievable at all. If developed, it would represent a major shift in economics, labor, and governance, requiring strict oversight and global coordination.
3. Artificial Superintelligence (ASI)
What is it?
Artificial Superintelligence (ASI) describes AI systems that surpass human intelligence in every dimension, including creativity, emotional understanding, scientific reasoning, and strategic planning.
ASI exists only as a concept. It is frequently discussed in AI safety literature and long-term risk analysis.
Current uses, apps, and services
None.ASI is not implemented in any system.
Future predictions
If ASI were ever created, it could drive breakthroughs in science and medicine—or pose serious existential risks. As a result, ASI is more relevant to ethics, policy, and long-term safety planning than practical development.
4. Self-Aware Artificial Intelligence
What is it?
Self-aware AI is a speculative concept in which machines possess consciousness, subjective experience, and a sense of self. This goes beyond intelligence into the realm of awareness.
There are no real examples. Self-aware AI is largely explored in philosophy, neuroscience, and speculative fiction.
Current uses, apps, and services
None. No AI system today has consciousness or self-awareness.
Future predictions
Most experts believe self-aware AI is far beyond current scientific understanding. Its discussion is valuable mainly for ethical debates and understanding the boundaries of intelligence.
II. AI Classification Based on Functionality
This framework focuses on how AI systems operate and interact with data and memory.
5. Reactive Machines
What is it?
Reactive machines respond only to present inputs. They do not store memories, learn from past experiences, or build internal models of the world.
IBM’s Deep Blue, the chess computer that defeated a world champion, is a classic example. It analyzed the board state but did not learn over time.
Current uses, apps, and services
-
Rule-based game engines
-
Simple automation systems
-
Deterministic control systems
Future predictions
Reactive machines will remain useful in highly controlled environments where predictability and reliability are more important than learning.
6. Limited Memory AI
What is it?
Limited Memory AI systems use past data and short-term memory to make decisions. They are trained on historical datasets and updated regularly.
A self-driving car that analyzes previous sensor data to predict pedestrian movement is a typical example.
Current uses, apps, and services
This is the most common form of AI today:
-
Autonomous vehicles
-
Recommendation algorithms
-
Fraud detection systems
-
Predictive analytics tools
Future predictions
Limited memory systems will become more data-efficient and context-aware, especially when combined with real-time learning and better simulation environments.
7. Theory of Mind AI
What is it?
Theory of Mind AI aims to understand human emotions, intentions, beliefs, and social behavior, enabling more natural interaction between humans and machines.
Experimental social robots that adjust responses based on user emotion are early examples.
Current uses, apps, and services
-
Research prototypes
-
Advanced conversational agents
-
Human–robot interaction experiments
Future predictions
As AI moves into education, healthcare, and mental health support, theory-of-mind capabilities will become increasingly important. However, widespread deployment is still years away.
8. Learning / Adaptive AI
What is it?
Adaptive AI systems can learn continuously from their environment and adjust their behavior in real time, often using reinforcement learning.
An AI trading system that adjusts its strategy based on market conditions is a common example.
Current uses, apps, and services
-
Autonomous trading bots
-
Robotics control systems
-
Real-time personalization engines
-
Adaptive cybersecurity systems
Future predictions
Adaptive AI will play a key role in automation, robotics, and decision-making systems, especially where environments are unpredictable.
